Blog / Globetrotter / Group
PATHOGENS: THE PROBLEM OF ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE (AMR)
Since the discovery of Antibiotics, millions of lives have been saved every year. However, some bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites – cumulatively known as pathogens – have evolved to become resistant to these antibiotic treatments. Globally these “superbugs” are on the rise and are now killing more people each year than either HIV/AIDS or malaria. […]
Since the discovery of Antibiotics, millions of lives have been saved every year. However, some bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites – cumulatively known as pathogens – have evolved to become resistant to these antibiotic treatments. Globally these “superbugs” are on the rise and are now killing more people each year than either HIV/AIDS or malaria.
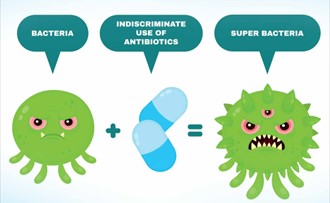
In 2019, drug-resistant infections directly killed 1.2 million people and played a role in 5 million more deaths worldwide. Deaths caused directly by antibiotic resistance are the highest in sub-Saharan Africa. Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) poses a major threat to human health around the world.
Major causes of AMR are overuse, misuse, and abuse of antibiotics, both in terms of; treatment plans/approach for pathogen infections in humans, and in the agricultural process of preparing the foods we eat. Even though there are other contributing factors to the problem, let’s focus on how we can mitigate the above.
A preventative approach to infections is the best way forward. Most infections are from ingested foods, hence, the need to prepare hygienically through the following ways:
- Separating raw and cooked foods
- Cook thoroughly
- Keep food at safe temperatures
- Use safe water and raw materials
What Individuals Can Do: ‘What can I do?’
- Observe general body hygiene and wellness through proper diet, cleanliness, avoiding close contact with sick people, practicing safer sex, active lifestyle, adequate sleep, and daily routines. This help boost your immune levels.
- Take antibiotics as and only when prescribed by a certified health professional. This excludes a pharmacist and self-treatment!
- Never demand antibiotics if your health worker says you don’t need them.
- Subsequently, never share or use leftover antibiotics.
What Health Professionals Can Do:
- Prevent infections by ensuring their hands, instruments, and environment are clean and sanitized.
- Only prescribe and dispense antibiotics when they are needed, according to current guidelines
- Report antibiotic-resistant infections to surveillance teams
- Talk to your patients about how to take antibiotics correctly, antibiotic resistance, and the dangers of misuse
- Talk to your patients about preventing infections (for example, vaccination, hand washing, safer sex, covering nose and mouth when sneezing)
What Policy Makers Can Do:
- Plan effectively to improve surveillance and strengthen infection prevention and control measures
- Regulate and promote the appropriate use and disposal of quality medicines
- Public awareness is key to make making appropriate improvements.
What The Agricultural Sector Can Do:
- Only give antibiotics to animals under veterinary supervision
- Eliminate the use of antibiotics for growth promotion or to prevent diseases in healthy animals
- Improve biosecurity on farms, hygiene, and animal welfare
To have a comprehensive understanding of the estimated AMR burden to date, read the below reference.
References:
Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: a systematic analysis. Articles| Volume 399, ISSUE 10325, P629-655, February 12, 2022
https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(21)02724-0/fulltext


